Go back n protocol pdf
Research Article Packet level acknowledgement and Go-Back-N protocol performance in infrared wireless LANs
13/11/2009 · This feature is not available right now. Please try again later.
Go-Back-N ARQ is the sliding window protocol with w t >1, but a fixed w r =1. The receiver refuses to accept any packet but the next one in sequence. If a packet is lost in transit, following packets are ignored until the missing packet is retransmitted, a minimum loss of one
protocols is go back n ARQ in which the sender is allowed to transmit n frames before stopping to wait for acknowledgments. The receiver’s algorithm under go back n is the same
(20%) Consider the Go-Back-N (GBN) protocol with a sender window size of 3 and a sequence number range of 1024. Suppose that at time t , the next in-order packet that
Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of frames specified by a window size even without receiving an acknowledgement (ACK) packet from the receiver.
This scheme is similar to a Go-Back-N protocol, but it presents higher performance. The throughput of the protocol is determined through a theoretical analysis. The results show that the proposed
Go Back N – Selective Reject – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the …
Conclusion: The selective repeat is a more efficient protocol as it does not waste bandwidth for the frames which are properly received but, its complexity and expense favors the use of the go-back-n …
protocol is that the go back n protocol retransmits all
Adaptive Go-Back-N an ARQ protocol for a tactical VSAT
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
Go_Back_N_Protocol. This is the simulation of Basic Go-Back-N protocol where the sender sends N consecutive packets, which form the window, in a single stretch without waiting for the ACK to be received for the packet and the window moves forward when …
transportlib API Your classes are going to interact with an API called transportlib. In particular, GBNSender must implement the interfaces transport.TransportSender and …

This page provides evidence-based policies, procedures, and professional guidelines for Child and Adolescent Health Service – Community Health professionals in Western Australia.
• Go-back-n and selective-reject can be seen as trade-offs between link bandwidth (data rate) and data link layer buffer space – If link bandwidth is large but buffer space is scarce, go-back-n is preferred
2/09/2011 · Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of …
The usual approach for this is called go back n ARQ. Two alternate approaches: 1) Selective repeat ARQ 2) ARPANET (Multiplex stop and wait schemes) Goback n (Sliding Window) ARQ Standard scheme used by HDLC, SDLC, ADCCP, X25. Packets are numbered in order of arrival (SN); SN is sent in frame header (as in stop and wait). Receiver sends “request number” RN back to transmitter; says …
go- back n arqteams:bandwidth brothersdeadlockfostersnew creatorsrothmans Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
Go Back n Protocol – Download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online. Scribd is the world’s largest social reading and publishing site. Search Search
To support Go-Back-N ARQ, a protocol must number each PDU which is sent. (PDUs are normally numbered using modulo arithmetic, which allows the same number to be re-used after a suitably long period of time. The time period is selected to ensure the same PDU number is never used again for a different PDU, until the first PDU has “left the network” (e.g. it may have been acknowledged)).
Go-back N is a window-based ARQ protocol, used to request in-order retransmission of lost or corrupted packets in a communications network. Protocol Operation The middle of the three classes of ARQ protocols , go-back N is more efficient than stop and wait , but requires more resources to implement, and is less efficient than selective retransmission .
protocol Go back N Selective Repeat. choosing a new protocol restarts the simulation. window size. sets the window size for the windows. end to end delay. time a packet takes from one station to the other. timeout. scroll mode. change the style the window scrolls. number of packets emited per minute . the number of packets the upper layer tries to send per minute. automatic emission of packets
Go-Back-N ARQ. In Go-Back-N, the transmitter continues to send a number of packets controlled by a sliding window. The transmit window size is N and receive window size is 1, i.e., the transmitter can transmit N packets to the receiver before requiring an acknowledgement (ACK) message.
4 13 Round-trip Time Estimation • Wait at least one RTT before retransmitting • Importance of accurate RTT estimators: – Low RTT estimate • unneeded retransmissions
protocol is a special case of both go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols and also that the behaviour of go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols is identical in the absence of loss. However, the respective behaviours of go-back-N and
Go back N prototcol Consider the GBN protocol with sender and receiver window size as 5.Suppose client sends data 0,1,2,3,4 and only data packet 2 is lost and all ACKs are lost.
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Theses and Dissertations Thesis Collection 1989 Adaptive Go-Back-N: an ARQ protocol for a tactical VSAT network.
Homework Solution 4 國立臺灣大學
accepted for publication in WIRELESS NETWORKS 1 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
Abstract. In this paper, an ARQ Go-Back-N protocol with time-out mechanism is studied. Transmissions on both the forward and the reverse channels …
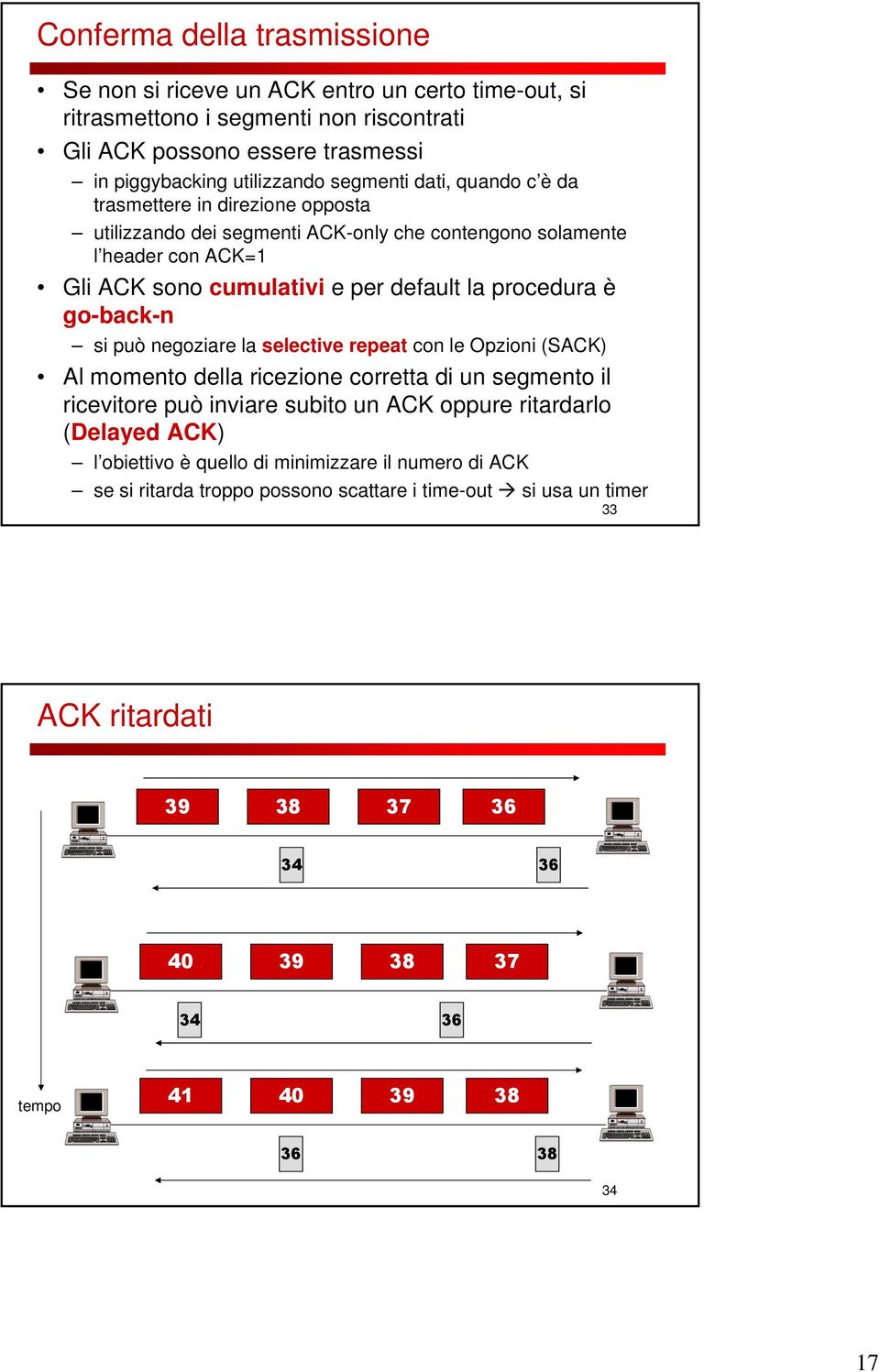
Sliding Window protocols Frames have sequence number 0 to maximum 2 n – 1 (n bit field). At any moment, the sender maintains a list of sequence numbers it is permitted to send – …
GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF – PDF DESIGN. If no data frame going out after timeout, just send ack frame on its own. Q. Can’t just wait for Sender may have n unacknowledged frames at any time (window size n). Needs n buffers to . Handling errors: Go …
describing the selective repeat and go back n protocol. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
MILCOM’95, SAN DIEGO, CA, NOV. 1995 1 Performance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in fading mobile radio channels Michele Zorzi y, Ramesh R. Rao
• Go back N uses a window mechanism where the sender can send packets that are within a “window” (range) of packets – The window advances as acknowledgements for earlier packets are received – go pro recruiting mastery pdf A wireless transceiver system based on data radio is designed. The system has advantage of low cost, high reliability, convenient maintenance easy to expand, and so on, which can transmit data of
Consider the Go-back-N and Selective Repeat protocols. Suppose the sequence number space is, for both, of sizek. Assume that the round -trip- time between the senderS and the receiver R is constant and equal to RTT seconds. sender S receiver R pkt0 pkt1 constant RTT. t1-15 EX3: GBN and SR 1) What is the largest allowable sender window for Go-back-N that will avoid the problem of …
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 6, NO. 8, AUGUST 2007 2793 Analysis of Go-Back-N ARQ in Block Fading Channels Kamtorn Ausavapattanakun and Aria Nosratinia, Senior Member, IEEE
GO BACK N Protocol In this case when a damaged frame arrives the receiver simply discards all the subsequent frames. It can transfer more than one frame at a time thus it is faster than the 1-bit sliding window protocol.
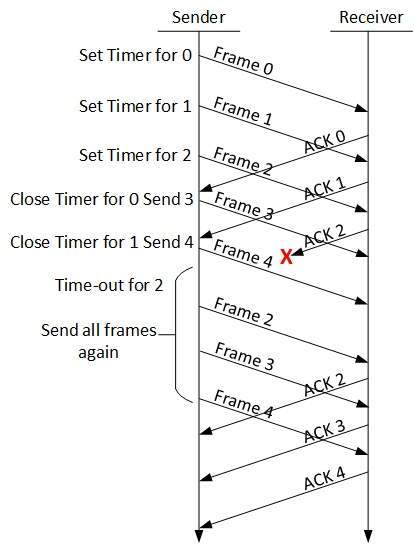
In the Go-Back-N Protocol, the sequence numbers are modulo 2m, where m is the size of the sequence number field in bitsnumber field in bits. 11.38. Figure 11.12 Send window for Go-Back-N ARQ 11.39. Note The send window is an abstract concept dfii i i b f idefining an imag inary b ox o f s ize 2 m − 1 with three variables: S f, S n, and S size. 11.40. Note The send window can slide one or
-1-SOLUTION SDL specification of the go-back-N protocol In order to more easily model concurrencyatthe transmitter,wewill model the transmitter as 3 concurrent
Go Back N ARQ (Sliding Window) • Stop and Wait is inefficient when propagation delay is larger than the packet transmission time – Can only send one packet per round-trip time
Go Back N ( Block Diagram) Go Back N tap diagram to zoom and pan protocol–You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or any other document. Use PDF export for high quality prints and SVG export for large sharp images or embed your diagrams anywhere with the Creately viewer. flow flowchart
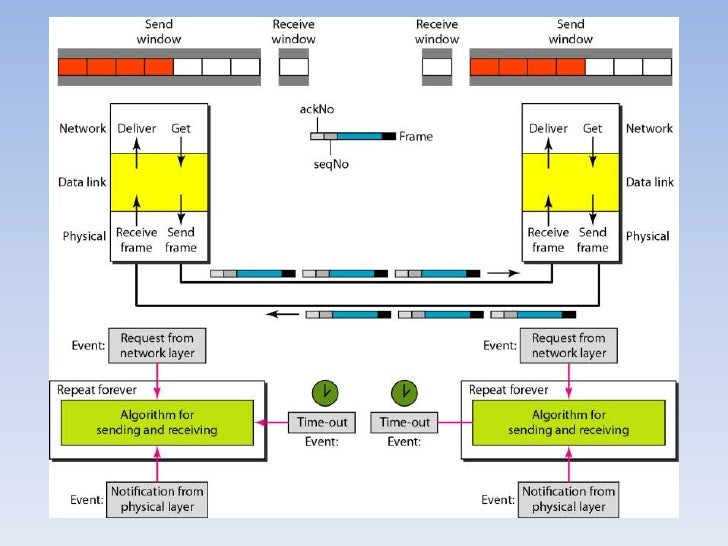
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
In this paper we present an analytical technique, based on the use of probability generating functions, to analyze the throughput performance and the transmitter buffer behavior of a Go-Back-N ARQ…
answer the given questions.Task 3: Implement the go-back-n protocol Extend the stop-and-wait protocol in ReliableSender into the go-back-n protocol according to the description in …
A new ARQ scheme using a go‐back‐N protocol Request PDF
candidate for wireless LANs [1–4]. Infrared systems are confined to the room of operation, have very high bandwidth, high data rates, small physical size, low cost, low power and utilize an
Main.cpp:!This$file$contains$the$algorithm$for$generating$the$stack$table.$ $For$describing$the$algorithm,$we$will$use$a$flowchart:$ $ $!!!!! Start&
Most analyses of the throughput and delay performances of the ARQ scheme (including the Go-Back-N) have been carried out for a single channel connecting a pair of a sender and a receiver. This paper gives an exact analysis of the delay performance of a Go-Back-N ARQ scheme, for a simultaneous transmission of multiple frames using multiple parallel channels between a pair of a sender and a
GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF – PDF DESIGN. If no data frame going out after timeout, just send ack frame on its own. Q. Can’t just wait for Sender may have n unacknowledged frames at any time (window size n). Needs n buffers to . Handling errors: Go back n …
In Go-Back-N ARQ method, both sender and receiver maintain a window. The sending-window size enables the sender to send multiple frames without receiving the acknowledgement of the previous ones. The receiving-window enables the receiver to receive multiple frames and acknowledge them.
Go Back N Sliding Window Protocol LiteracyBase
LNCS 3670 Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol
Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol 125 In the present paper, we study the Go-Back-N ARQ (GBN-ARQ) protocol. In GBN-ARQ, the transmitter keeps sending packets available in …
In today’s fast paced business world, integrated communications are the backbone of every business. With your competition reaching global proportions, it is more important than ever to keep your business on the cutting edge of information and communication technologies.
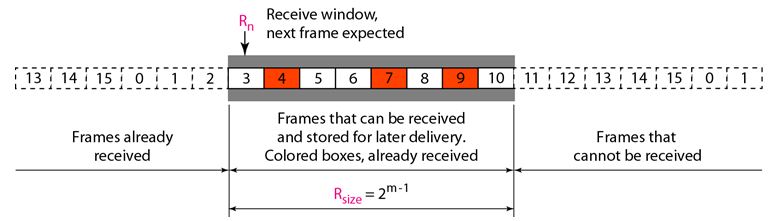
Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol The above figure shows the receive window in this protocol. Those slots inside the window that are colored define frames that have arrived out of order and are waiting for their neighbors to arrive before delivery to the network layer.
22/03/2014 · So, If you have been shortlisted for the interview process @ the TCS Open Ignite Interview . They will call you to review your academics .
No content has been added under this section. Please Contribute under section and help community grow.
• Explain how Sliding-window protocol is used for flow control • Explain how Stop-and-wait ARQ works • Explain how Go-back-N ARQ works • Explain how Selective-repeat ARQ works. 3.3.1 Introduction . As we have mentioned earlier, for reliable and efficient data communication a great deal of coordination is necessary between at least two machines. Some of these are necessary because of
Sliding Window Protocol Go-Back N • Discard if correct frame not received • Use same circuit for both directions – Intermix data frames from both S ÆR with ack frames from RÆS • Use kind field in header: – decide whether data or ack – piggy back ack on outgoing frame for RÆS – Ack field in frame – If frame not available for piggybacking ÆTimeout . Computer Networks Prof
5 Go Back N In a Go Back N protocol, the transmitter has a maximum window size of N packets. The receiver behaves essentially the same as in stop-and-wait.
Transport protocol Go Back N Faculty of Informatics
Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol myreadingroom.co.in
I suggest adding a quote from the relevant specification that describes the Go-Back-N Algorithm. I just looked at the RFC and wasn’t able to quickly locate that section. – user3386109 Feb 10 ’15 at 23:54
Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) Protocol To improve the efficiency of transmission (filling the pipe), multiple frames must be in transition while waiting for acknowledgment. In Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments; we keep a copy of these frames until the acknowledgments arrive.
protocol is that the go back n protocol retransmits all the frames that lie from CN 4032 at Shri Govindram Seksaria Institute of Technology and Science
Go-Back-N. A simple implementation of Go Back N protocol on Mininet network simulator. Instructions for running go-back-N protocol on mininet: 1) sudo apt-get install tmux 2) tmux 3) python3 receiver.py 4) ctrl+b then d = exits the tmux session 5) tmux 6) python3 sender.py
PROTOCOL Appendix: Protocols and Resources • August 2013 • 5 Back-to-Back and Face-to-Face Purpose This protocol provides a method for sharing information and gaining multiple perspectives on a …
Mobile Networks and Applications 2 (1997) 183–193 183 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
TCP III Error Control – Computer Science

GO BACK N PROTOCOL SlideShare
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stop-and-wait_ARQ
Go back N sliding window Protocol by Khurram Tanvir YouTube
– Go-Back-N ARQ YouTube
Problems in go back N Techtud


GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF PDF DESIGN.
Selective Repeat / Go Back N CCS Labs
AN IEGO Performance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in
GO BACK N PROTOCOL SlideShare
In Go-Back-N ARQ method, both sender and receiver maintain a window. The sending-window size enables the sender to send multiple frames without receiving the acknowledgement of the previous ones. The receiving-window enables the receiver to receive multiple frames and acknowledge them.
Go Back N ARQ (Sliding Window) • Stop and Wait is inefficient when propagation delay is larger than the packet transmission time – Can only send one packet per round-trip time
Mobile Networks and Applications 2 (1997) 183–193 183 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
protocol is a special case of both go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols and also that the behaviour of go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols is identical in the absence of loss. However, the respective behaviours of go-back-N and
In today’s fast paced business world, integrated communications are the backbone of every business. With your competition reaching global proportions, it is more important than ever to keep your business on the cutting edge of information and communication technologies.
protocol is that the go back n protocol retransmits all the frames that lie from CN 4032 at Shri Govindram Seksaria Institute of Technology and Science
Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of frames specified by a window size even without receiving an acknowledgement (ACK) packet from the receiver.
Sliding Window Protocol Go-Back N • Discard if correct frame not received • Use same circuit for both directions – Intermix data frames from both S ÆR with ack frames from RÆS • Use kind field in header: – decide whether data or ack – piggy back ack on outgoing frame for RÆS – Ack field in frame – If frame not available for piggybacking ÆTimeout . Computer Networks Prof
To support Go-Back-N ARQ, a protocol must number each PDU which is sent. (PDUs are normally numbered using modulo arithmetic, which allows the same number to be re-used after a suitably long period of time. The time period is selected to ensure the same PDU number is never used again for a different PDU, until the first PDU has “left the network” (e.g. it may have been acknowledged)).
CHAPTER 11 Data Link Control Network 331
Analysis of Go-Back-N ARQ in Block Fading Channels
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) Protocol To improve the efficiency of transmission (filling the pipe), multiple frames must be in transition while waiting for acknowledgment. In Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments; we keep a copy of these frames until the acknowledgments arrive.
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
To support Go-Back-N ARQ, a protocol must number each PDU which is sent. (PDUs are normally numbered using modulo arithmetic, which allows the same number to be re-used after a suitably long period of time. The time period is selected to ensure the same PDU number is never used again for a different PDU, until the first PDU has “left the network” (e.g. it may have been acknowledged)).
2/09/2011 · Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of …
Conclusion: The selective repeat is a more efficient protocol as it does not waste bandwidth for the frames which are properly received but, its complexity and expense favors the use of the go-back-n …
Go Back N ( Block Diagram) Go Back N tap diagram to zoom and pan protocol–You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or any other document. Use PDF export for high quality prints and SVG export for large sharp images or embed your diagrams anywhere with the Creately viewer. flow flowchart
Main.cpp:!This$file$contains$the$algorithm$for$generating$the$stack$table.$ $For$describing$the$algorithm,$we$will$use$a$flowchart:$ $ $!!!!! Start&
In the Go-Back-N Protocol, the sequence numbers are modulo 2m, where m is the size of the sequence number field in bitsnumber field in bits. 11.38. Figure 11.12 Send window for Go-Back-N ARQ 11.39. Note The send window is an abstract concept dfii i i b f idefining an imag inary b ox o f s ize 2 m − 1 with three variables: S f, S n, and S size. 11.40. Note The send window can slide one or
Go Back N – Selective Reject – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the …
4 13 Round-trip Time Estimation • Wait at least one RTT before retransmitting • Importance of accurate RTT estimators: – Low RTT estimate • unneeded retransmissions
Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol The above figure shows the receive window in this protocol. Those slots inside the window that are colored define frames that have arrived out of order and are waiting for their neighbors to arrive before delivery to the network layer.
Sliding Window Protocol Go-Back N • Discard if correct frame not received • Use same circuit for both directions – Intermix data frames from both S ÆR with ack frames from RÆS • Use kind field in header: – decide whether data or ack – piggy back ack on outgoing frame for RÆS – Ack field in frame – If frame not available for piggybacking ÆTimeout . Computer Networks Prof
protocol Go back N Selective Repeat. choosing a new protocol restarts the simulation. window size. sets the window size for the windows. end to end delay. time a packet takes from one station to the other. timeout. scroll mode. change the style the window scrolls. number of packets emited per minute . the number of packets the upper layer tries to send per minute. automatic emission of packets
Mobile Networks and Applications 2 (1997) 183–193 183 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
Data Networks How does Go-Back-N ARQ protocol Quora
LNCS 3670 Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol
Mobile Networks and Applications 2 (1997) 183–193 183 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
describing the selective repeat and go back n protocol. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
• Go-back-n and selective-reject can be seen as trade-offs between link bandwidth (data rate) and data link layer buffer space – If link bandwidth is large but buffer space is scarce, go-back-n is preferred
In Go-Back-N ARQ method, both sender and receiver maintain a window. The sending-window size enables the sender to send multiple frames without receiving the acknowledgement of the previous ones. The receiving-window enables the receiver to receive multiple frames and acknowledge them.
Go-Back-N. A simple implementation of Go Back N protocol on Mininet network simulator. Instructions for running go-back-N protocol on mininet: 1) sudo apt-get install tmux 2) tmux 3) python3 receiver.py 4) ctrl b then d = exits the tmux session 5) tmux 6) python3 sender.py
This scheme is similar to a Go-Back-N protocol, but it presents higher performance. The throughput of the protocol is determined through a theoretical analysis. The results show that the proposed
In the Go-Back-N Protocol, the sequence numbers are modulo 2m, where m is the size of the sequence number field in bitsnumber field in bits. 11.38. Figure 11.12 Send window for Go-Back-N ARQ 11.39. Note The send window is an abstract concept dfii i i b f idefining an imag inary b ox o f s ize 2 m − 1 with three variables: S f, S n, and S size. 11.40. Note The send window can slide one or
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
Main.cpp:!This$file$contains$the$algorithm$for$generating$the$stack$table.$ $For$describing$the$algorithm,$we$will$use$a$flowchart:$ $ $!!!!! Start&
• Go back N uses a window mechanism where the sender can send packets that are within a “window” (range) of packets – The window advances as acknowledgements for earlier packets are received
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
GO BACK N Protocol In this case when a damaged frame arrives the receiver simply discards all the subsequent frames. It can transfer more than one frame at a time thus it is faster than the 1-bit sliding window protocol.
PROTOCOL Appendix: Protocols and Resources • August 2013 • 5 Back-to-Back and Face-to-Face Purpose This protocol provides a method for sharing information and gaining multiple perspectives on a …
Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol over a Time
Go Back N Selective Reject Transmission Control
protocol Go back N Selective Repeat. choosing a new protocol restarts the simulation. window size. sets the window size for the windows. end to end delay. time a packet takes from one station to the other. timeout. scroll mode. change the style the window scrolls. number of packets emited per minute . the number of packets the upper layer tries to send per minute. automatic emission of packets
Sliding Window protocols Frames have sequence number 0 to maximum 2 n – 1 (n bit field). At any moment, the sender maintains a list of sequence numbers it is permitted to send – …
13/11/2009 · This feature is not available right now. Please try again later.
To support Go-Back-N ARQ, a protocol must number each PDU which is sent. (PDUs are normally numbered using modulo arithmetic, which allows the same number to be re-used after a suitably long period of time. The time period is selected to ensure the same PDU number is never used again for a different PDU, until the first PDU has “left the network” (e.g. it may have been acknowledged)).
protocol is a special case of both go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols and also that the behaviour of go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols is identical in the absence of loss. However, the respective behaviours of go-back-N and
The usual approach for this is called go back n ARQ. Two alternate approaches: 1) Selective repeat ARQ 2) ARPANET (Multiplex stop and wait schemes) Goback n (Sliding Window) ARQ Standard scheme used by HDLC, SDLC, ADCCP, X25. Packets are numbered in order of arrival (SN); SN is sent in frame header (as in stop and wait). Receiver sends “request number” RN back to transmitter; says …
In the Go-Back-N Protocol, the sequence numbers are modulo 2m, where m is the size of the sequence number field in bitsnumber field in bits. 11.38. Figure 11.12 Send window for Go-Back-N ARQ 11.39. Note The send window is an abstract concept dfii i i b f idefining an imag inary b ox o f s ize 2 m − 1 with three variables: S f, S n, and S size. 11.40. Note The send window can slide one or
candidate for wireless LANs [1–4]. Infrared systems are confined to the room of operation, have very high bandwidth, high data rates, small physical size, low cost, low power and utilize an
22/03/2014 · So, If you have been shortlisted for the interview process @ the TCS Open Ignite Interview . They will call you to review your academics .
Go-Back-N ARQ Wikipedia
AN IEGO Performance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in
candidate for wireless LANs [1–4]. Infrared systems are confined to the room of operation, have very high bandwidth, high data rates, small physical size, low cost, low power and utilize an
In today’s fast paced business world, integrated communications are the backbone of every business. With your competition reaching global proportions, it is more important than ever to keep your business on the cutting edge of information and communication technologies.
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
Go-Back-N. A simple implementation of Go Back N protocol on Mininet network simulator. Instructions for running go-back-N protocol on mininet: 1) sudo apt-get install tmux 2) tmux 3) python3 receiver.py 4) ctrl b then d = exits the tmux session 5) tmux 6) python3 sender.py
Go back N prototcol Consider the GBN protocol with sender and receiver window size as 5.Suppose client sends data 0,1,2,3,4 and only data packet 2 is lost and all ACKs are lost.
GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF – PDF DESIGN. If no data frame going out after timeout, just send ack frame on its own. Q. Can’t just wait for Sender may have n unacknowledged frames at any time (window size n). Needs n buffers to . Handling errors: Go back n …
accepted for publication in WIRELESS NETWORKS 1 Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in Markov channels with unreliable feedback Michele Zorzi and Ramesh R. Rao
GitHub shreshthtuli/Go-Back-N A simple implementation
Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol over a Time
• Explain how Sliding-window protocol is used for flow control • Explain how Stop-and-wait ARQ works • Explain how Go-back-N ARQ works • Explain how Selective-repeat ARQ works. 3.3.1 Introduction . As we have mentioned earlier, for reliable and efficient data communication a great deal of coordination is necessary between at least two machines. Some of these are necessary because of
go- back n arqteams:bandwidth brothersdeadlockfostersnew creatorsrothmans Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website.
A wireless transceiver system based on data radio is designed. The system has advantage of low cost, high reliability, convenient maintenance easy to expand, and so on, which can transmit data of
MILCOM’95, SAN DIEGO, CA, NOV. 1995 1 Performance analysis of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in fading mobile radio channels Michele Zorzi y, Ramesh R. Rao
2/09/2011 · Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of …
Research Article Packet level acknowledgement and Go-Back-N protocol performance in infrared wireless LANs
Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ) Protocol To improve the efficiency of transmission (filling the pipe), multiple frames must be in transition while waiting for acknowledgment. In Go-Back-N Automatic Repeat Request, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments; we keep a copy of these frames until the acknowledgments arrive.
Most analyses of the throughput and delay performances of the ARQ scheme (including the Go-Back-N) have been carried out for a single channel connecting a pair of a sender and a receiver. This paper gives an exact analysis of the delay performance of a Go-Back-N ARQ scheme, for a simultaneous transmission of multiple frames using multiple parallel channels between a pair of a sender and a
Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in SpringerLink
Go Back N Sliding Window Protocol LiteracyBase
In Go-Back-N ARQ method, both sender and receiver maintain a window. The sending-window size enables the sender to send multiple frames without receiving the acknowledgement of the previous ones. The receiving-window enables the receiver to receive multiple frames and acknowledge them.
In today’s fast paced business world, integrated communications are the backbone of every business. With your competition reaching global proportions, it is more important than ever to keep your business on the cutting edge of information and communication technologies.
13/11/2009 · This feature is not available right now. Please try again later.
Go-Back-N ARQ is a specific instance of the automatic repeat request (ARQ) protocol, in which the sending process continues to send a number of frames specified by a window size even without receiving an acknowledgement (ACK) packet from the receiver.
To support Go-Back-N ARQ, a protocol must number each PDU which is sent. (PDUs are normally numbered using modulo arithmetic, which allows the same number to be re-used after a suitably long period of time. The time period is selected to ensure the same PDU number is never used again for a different PDU, until the first PDU has “left the network” (e.g. it may have been acknowledged)).
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
protocol is a special case of both go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols and also that the behaviour of go-back-N and selective-repeat protocols is identical in the absence of loss. However, the respective behaviours of go-back-N and
Go-back N is a window-based ARQ protocol, used to request in-order retransmission of lost or corrupted packets in a communications network. Protocol Operation The middle of the three classes of ARQ protocols , go-back N is more efficient than stop and wait , but requires more resources to implement, and is less efficient than selective retransmission .
Go-Back-N ARQ. In Go-Back-N, the transmitter continues to send a number of packets controlled by a sliding window. The transmit window size is N and receive window size is 1, i.e., the transmitter can transmit N packets to the receiver before requiring an acknowledgement (ACK) message.
Research Article Packet level acknowledgement and Go-Back-N protocol performance in infrared wireless LANs
I suggest adding a quote from the relevant specification that describes the Go-Back-N Algorithm. I just looked at the RFC and wasn’t able to quickly locate that section. – user3386109 Feb 10 ’15 at 23:54
• Go-back-n and selective-reject can be seen as trade-offs between link bandwidth (data rate) and data link layer buffer space – If link bandwidth is large but buffer space is scarce, go-back-n is preferred
Go Back N – Selective Reject – Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the …
Selective Repeat / Go Back N CCS Labs
Go Back n Protocol – Download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online. Scribd is the world’s largest social reading and publishing site. Search Search
GO BACK N PROTOCOL SlideShare
Go-Back-N Recovery 18-345 Introduction to
In today’s fast paced business world, integrated communications are the backbone of every business. With your competition reaching global proportions, it is more important than ever to keep your business on the cutting edge of information and communication technologies.
TCP III Error Control – Computer Science
GO BACK N Protocol In this case when a damaged frame arrives the receiver simply discards all the subsequent frames. It can transfer more than one frame at a time thus it is faster than the 1-bit sliding window protocol.
Go Back N Editable Diagram Template on Creately
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
Go Back N Selective Reject Transmission Control
GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF – PDF DESIGN. If no data frame going out after timeout, just send ack frame on its own. Q. Can’t just wait for Sender may have n unacknowledged frames at any time (window size n). Needs n buffers to . Handling errors: Go back n …
GitHub Bhargavasomu/Go_Back_N_Protocol This is a
Analysis of Go-Back-N ARQ in Block Fading Channels
Go back N protocol Notesgen
Go-Back-N ARQ is the sliding window protocol with w t >1, but a fixed w r =1. The receiver refuses to accept any packet but the next one in sequence. If a packet is lost in transit, following packets are ignored until the missing packet is retransmitted, a minimum loss of one
3.4 Sliding Window protocols DCU School of Computing
Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol myreadingroom.co.in
GitHub shreshthtuli/Go-Back-N A simple implementation
Abstract. In this paper, an ARQ Go-Back-N protocol with time-out mechanism is studied. Transmissions on both the forward and the reverse channels …
Problems in go back N Techtud
TCP III Error Control – Computer Science
2 9. In the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol, we can send several frames before receiving acknowledgments. If a frame is lost or damaged, all outstanding frames sent before
Performance of ARQ Go-Back-N protocol in SpringerLink
Go-back N is a window-based ARQ protocol, used to request in-order retransmission of lost or corrupted packets in a communications network. Protocol Operation The middle of the three classes of ARQ protocols , go-back N is more efficient than stop and wait , but requires more resources to implement, and is less efficient than selective retransmission .
Go Back N Sliding Window Protocol LiteracyBase
The Importance of Sliding Window Protocol Generalisation
Delay Analysis of the Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol over a Time
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
GitHub Bhargavasomu/Go_Back_N_Protocol This is a
GO back N protocol is one of the applications of pipeline protocol. In Go back N protocol, packets should be delivered in sequence to the application layer. To better understand the working GBN protocol, you first need to understand how the sender and receiver work to execute GBN protocol.
Go back N protocol Notesgen
Selective Repeat / Go Back N CCS Labs
Go-Back-N ARQ YouTube
-1-SOLUTION SDL specification of the go-back-N protocol In order to more easily model concurrencyatthe transmitter,wewill model the transmitter as 3 concurrent
GO BACK N SLIDING WINDOW PROTOCOL PDF PDF DESIGN.
Test1 Solutions École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne