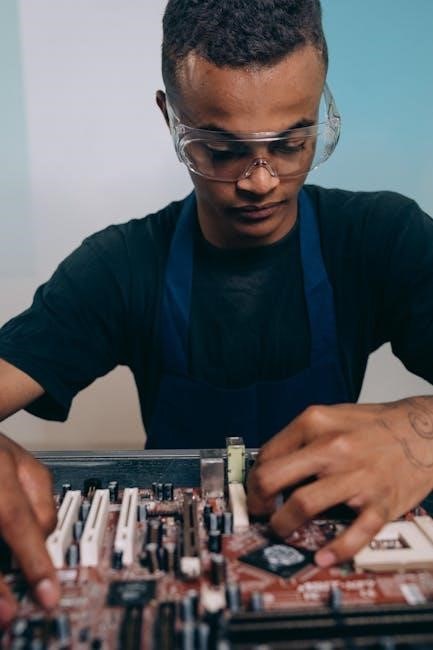
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules are the cornerstone for electrical installations in Australia and New Zealand, providing essential safety and design standards for all practitioners.
1.1 What Are the AS 3000 Wiring Rules?
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules are a joint Australian and New Zealand standard that provides the technical requirements for the design, construction, and verification of electrical installations. These rules ensure safety, reliability, and compliance for all electrical systems, covering both residential and commercial applications. The standard is developed by the Joint Technical Committee EL-001 and is regularly updated to incorporate new technologies and safety measures. Compliance with AS/NZS 3000 is mandatory for electricians and professionals in the field, ensuring that electrical installations meet the highest safety standards. The rules also include guidelines for selecting and installing electrical equipment, ensuring protection against hazards and adherence to best practices.
1.2 Importance of the Standard
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand. They establish uniform standards, reducing risks associated with electrical hazards and promoting consistency in practices. Compliance with these rules is legally required, protecting both professionals and end-users. By adhering to the standard, electricians ensure their work meets rigorous safety benchmarks, minimizing potential dangers. The rules also serve as a foundational guide for industry professionals, offering clear frameworks for design, construction, and verification processes. Ultimately, the standard safeguards lives and property while maintaining trust in electrical systems throughout both countries.
History and Evolution of the Standard
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules have evolved significantly since their inception, with major updates in 2007, 2018, and subsequent amendments in 2020 and 2021 to enhance safety and clarity.
2.1 Evolution of the AS/NZS 3000
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules have undergone significant transformations since their establishment, reflecting advancements in technology and safety requirements. The standard was first introduced to provide a unified framework for electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand. Over the years, it has been periodically updated to address emerging challenges and incorporate new technologies. Key milestones include the 2007 edition, which introduced major revisions, and the 2018 edition, published in June 2018, which became mandatory from January 2019. These updates ensure the standard remains relevant and effective in safeguarding electrical systems.
2.2 Key Milestones in Updates
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules have seen several pivotal updates, enhancing safety and clarity. The 2007 edition introduced major revisions, aligning with modern electrical practices. In 2018, the standard was published in June and became mandatory from January 2019, incorporating significant changes. A 2020 amendment addressed consistency issues and provided clarifications, while a 2021 update further refined requirements. These milestones reflect ongoing efforts to adapt to technological advancements and industry needs, ensuring the standard remains a reliable guide for safe electrical installations.

Key Changes in the 2018 Edition
The 2018 edition introduced significant updates, including new definitions, revised installation practices, and enhanced safety measures to align with modern electrical technologies and practices.
3.1 Significant Updates from Previous Versions
The 2018 edition of AS/NZS 3000 introduced substantial changes, including new and revised definitions in Clause 1.4, marked by asterisks for clarity. These updates aimed to enhance safety, incorporating modern electrical technologies. Key revisions addressed installation practices, such as isolation switches for air conditioners, requiring readily accessible, lockable switches not mounted on the units. Neutral switching was clarified as unnecessary but permissible. The standard also improved consistency and provided clearer guidelines for electricians, ensuring safer and more efficient electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand. These changes reflect the evolving needs of the industry, emphasizing adherence to updated safety protocols and design principles.
3.2 Impact on Electrical Installations
The 2018 AS/NZS 3000 updates significantly influenced electrical installations by enhancing safety and clarity. Changes mandated lockable isolation switches for air conditioners, improving accessibility and compliance. Neutral switching was clarified as optional, reducing confusion. These revisions streamlined installation processes, ensuring safer and more efficient systems. Electricians benefited from clearer guidelines, enabling better adherence to standards. The updates also addressed modern technologies, ensuring installations remain current and safe. Overall, the changes promoted consistency, reduced risks, and aligned practices with international standards, benefiting both professionals and end-users. These impacts underscored the importance of adopting the latest Wiring Rules for reliable and compliant electrical systems across Australia and New Zealand.
2020 and 2021 Amendments
The 2020 and 2021 amendments to AS/NZS 3000 addressed consistency issues, provided clarifications, and updated safety standards, ensuring the Wiring Rules remained aligned with modern electrical practices and technologies.
4.1 Clarifications and Additions in 2020
The 2020 amendment to AS/NZS 3000 introduced key clarifications and additions to enhance the standard’s consistency and applicability. Changes were marked with a marginal bar for easy identification. These updates addressed areas such as safe electrical practices, material selection, and installation methods. New clauses were added to improve clarity on specific wiring scenarios, ensuring better compliance and safety outcomes. The amendment also refined requirements for verification and testing processes, aligning the standard with modern electrical technologies and practices. These adjustments were crucial for maintaining the standard’s relevance and effectiveness in ensuring safe electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand.
4.2 Further Updates in 2021
In 2021, additional updates were made to the AS/NZS 3000 standard, focusing on specific technical clarifications and enhancements. These changes aimed to address emerging technologies and industry needs. The updates included revisions to clauses related to electrical installation verification and testing procedures, ensuring compliance with current safety standards. New guidelines were introduced for low-voltage electrical installations, particularly in residential and commercial settings. The amendments also streamlined documentation requirements, making it easier for electricians to adhere to the standard. These updates were implemented to maintain the standard’s alignment with global best practices and to ensure continued safety and efficiency in electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand.

Structure of the Standard
The AS/NZS 3000 standard is structured into clear sections and appendices, ensuring logical flow from definitions to practical applications, with appendices providing supplementary guidance and examples.
5;1 Organization of the Document
The AS/NZS 3000 standard is systematically organized into clear sections and appendices, ensuring a logical flow. The document begins with definitions and fundamental principles, followed by detailed requirements for electrical installations. Changes in the 2018 edition are marked with an asterisk or marginal bars for easy identification. The standard includes clauses and tables that guide the selection and installation of electrical equipment. Appendices provide supplementary information and examples to support practical applications. Published on 26 June 2018, it supersedes the 2007 version, incorporating amendments from 2020 and 2021 to enhance clarity and safety. This structured approach ensures that electricians and professionals can navigate and apply the rules effectively.
5.2 Sections and Appendices Overview
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules are divided into clear sections and appendices, each serving a specific purpose. The main sections cover definitions, installation requirements, safety principles, and compliance guidelines. Appendices provide supplementary information, such as diagrams, examples, and additional resources, to aid in understanding complex topics. The appendices are optional but highly recommended for deeper insights. The 2018 edition includes updates marked by asterisks or marginal bars, indicating significant changes. Amendments from 2020 and 2021 are also incorporated, enhancing clarity and safety standards. This structured format ensures that electricians and professionals can easily navigate and apply the rules effectively in their work.
Safety Requirements and Standards
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules emphasize fundamental safety principles, ensuring electrical installations are designed to protect people and property from hazards. Compliance with these standards is mandatory.
6.1 Fundamental Safety Principles
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules establish core safety principles to ensure electrical installations protect people, livestock, and property from electric shock, thermal effects, and other hazards. These principles emphasize proper design, installation, and verification methods to maintain safety under normal operating conditions and foreseeable faults. The standard requires adherence to safe practices, such as correct cable sizing, proper earthing, and isolation procedures. It also addresses emergency procedures and equipment protection. Compliance with these principles ensures installations are inherently safe and resilient. The 2018 edition, along with its 2020 and 2021 amendments, reinforces these fundamentals, making them indispensable for electricians and designers. Adherence is mandatory to prevent risks and ensure reliability.
6.2 Compliance and Risk Management
Compliance with the AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules is mandatory to ensure electrical installations meet safety and performance requirements. The standard outlines legal obligations for electricians and designers, emphasizing adherence to prescribed practices. Risk management is central, requiring identification and mitigation of potential hazards to prevent electrical shocks, fires, and other dangers. Installations must be designed to withstand foreseeable faults, with proper documentation and testing to verify compliance. Non-compliance can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, and compromised safety. Regular updates, such as the 2020 and 2021 amendments, address emerging risks and clarify requirements, ensuring the standard remains robust and aligned with industry needs. Adherence to these guidelines is essential for protecting lives and property while avoiding legal repercussions.

Residential vs. Commercial Wiring
AS 3000 Wiring Rules differentiate between residential and commercial wiring, addressing unique requirements for safety, load calculations, and circuit design to ensure efficiency and compliance in both settings.
7.1 Differences in Application
The AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules outline distinct application requirements for residential and commercial wiring. Residential installations focus on single-phase systems, household appliances, and safety for private use. In contrast, commercial environments require three-phase systems, higher power capacities, and more complex circuit designs. Specific considerations include load calculations, earthing methods, and isolation switches. Commercial settings may also involve hazardous areas and specialized equipment, necessitating stricter adherence to safety protocols. These differences ensure tailored approaches for each type of installation, optimizing functionality and safety while addressing the unique demands of each environment
7.2 Specific Considerations for Each
Residential wiring under AS/NZS 3000 requires attention to home safety, with mandatory RCD protection and clear isolation points. Commercial installations demand higher fault tolerance, surge protection, and compliance with workplace safety standards. Residential projects often involve simpler circuits, while commercial settings may require complex cabling, data networks, and emergency systems. Specific considerations include load diversity, voltage drop calculations, and equipment selection based on environment. Both sectors must adhere to earthing and bonding requirements, but commercial applications may additionally involve hazardous zones and explosive atmospheres, necessitating specialized materials and practices to ensure compliance and safety

Installation and Testing Procedures
AS/NZS 3000 outlines precise installation steps, including material selection and proper connections. Testing involves voltage, insulation, and earth continuity checks to ensure compliance and safety standards
8.1 Best Practices for Installations
Adhering to AS/NZS 3000:2018 ensures safe and efficient electrical installations. Best practices include proper material selection, correct sizing of conductors, and secure connections. Electricians must follow verified installation techniques, such as installing cables at appropriate heights and distances from hazards. Ensuring insulation integrity and proper earthing is critical. Regular inspection of tools and equipment prevents faulty installations. Compliance with safety standards, like lockable isolation switches, is mandatory. Detailed documentation of the installation process aids in future maintenance and compliance checks. By following these guidelines, electricians minimize risks and ensure systems operate reliably. Proper training and staying updated on amendments are essential for adherence to these best practices.
Testing and verification are crucial steps in ensuring compliance with AS/NZS 3000:2018. Electricians must conduct thorough inspections and tests, including earth fault loop impedance and insulation resistance checks. Detailed records must be maintained, documenting all test results. Verification processes ensure installations meet safety and performance standards, preventing potential hazards. Regular updates to testing procedures, as per amendments, are essential for compliance. Proper documentation aids in audits and future maintenance. By adhering to these processes, electricians ensure reliable and safe electrical systems, minimizing risks and ensuring long-term functionality. Compliance with testing standards is non-negotiable, safeguarding both installations and users. Accurate records also facilitate traceability and accountability in the event of issues. This systematic approach upholds the integrity of electrical installations nationwide. Compliance with AS/NZS 3000 is mandatory, enforced through inspections and penalties for non-adherence. Authorities ensure installations meet legal standards, protecting safety and reliability in electrical systems nationwide. Adherence to AS/NZS 3000 is legally required for all electrical installations in Australia and New Zealand. The standard is enforced by regulatory bodies, ensuring compliance through regular inspections and audits. Non-compliance can result in penalties, fines, or even legal action. The legal framework mandates that all electricians and installers follow the outlined rules to guarantee safety and reliability. This includes proper documentation, testing, and verification processes. Compliance certifications are necessary for project approval, and any deviations from the standard can lead to severe consequences. The legal requirements emphasize the importance of following the Wiring Rules to protect both people and property. Strict enforcement ensures uniformity and accountability across the industry. Non-compliance with AS/NZS 3000 Wiring Rules can lead to severe legal, financial, and reputational consequences. Electricians and businesses may face penalties, fines, or even legal action for violating safety standards. Projects that fail to meet the requirements can be rejected, requiring costly corrections or even complete reinstallation. Non-compliance also poses significant safety risks, potentially leading to electrical hazards, injuries, or fatalities. In such cases, professionals may be held liable for damages or losses. Additionally, repeated non-compliance can result in loss of licensure or certifications, damaging a professional’s reputation and ability to secure future projects. The financial and operational impacts underscore the importance of strict adherence to the Wiring Rules. Electricians can access the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF, along with supplementary guides and materials, to ensure compliance and understanding of the standard’s requirements effectively. The AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF is readily available for electricians and professionals through official sources like Standards Australia and New Zealand. It is essential to obtain the document from reputable platforms to ensure authenticity and compliance. The PDF provides a comprehensive guide to the standard, including updates and amendments, such as those from 2020 and 2021. Electricians are encouraged to refer to the latest version to stay informed about current regulations. Additionally, the document is structured logically, making it easier to navigate and apply the rules effectively in various electrical installations. Supplementary materials and guides complement the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF, offering deeper insights and practical applications. These resources include detailed technical notes, diagrams, and case studies to aid electricians in complex installations. The official standards websites provide additional documents, such as amendment summaries and interpretation guides. Training courses and webinars are also available, focusing on specific aspects like cable sizing and safety protocols. These materials ensure professionals stay updated and can apply the rules effectively, addressing challenges in both residential and commercial settings while maintaining compliance with the latest standards. They are invaluable for enhancing understanding and ensuring safe, efficient electrical work. Common queries include understanding updates in the 2018 edition, interpreting specific clauses, and clarifications on compliance requirements, all addressed to ensure adherence to the standard effectively. Common questions about the AS 3000 Wiring Rules often revolve around accessing the standard, understanding updates, and interpreting specific clauses. Many seek clarity on the 2018 edition’s changes, such as new definitions and amended requirements. Electricians frequently inquire about compliance with safety principles and risk management practices. Another common query is how to apply the standard to residential vs. commercial installations, with a focus on installation best practices. Additionally, there is interest in the 2020 and 2021 amendments, particularly regarding clarifications on consistency and updates to testing procedures. Professionals also ask about resources, such as where to find the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF and supplementary guides to ensure they are up-to-date with the latest requirements. Typical confusions about the AS 3000 Wiring Rules often stem from interpreting specific clauses, updates, and practical application. The 2020 and 2021 amendments introduced changes that clarify previous ambiguities, particularly in sections related to safety and installation practices. Another common confusion is understanding the differences between residential and commercial wiring standards, which the AS 3000 addresses by providing distinct guidelines for each. Additionally, the standard’s structure and supplementary materials help professionals navigate complex requirements. Resources like the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF, official guides, training courses, and certification programs are essential for resolving these confusions and ensuring compliance. Real-world projects demonstrate the practical application of AS 3000 Wiring Rules, showcasing compliance challenges and solutions. Case studies highlight lessons learned, ensuring safer electrical installations across various industries. The AS 3000 Wiring Rules are applied across various sectors, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical installations. From residential homes to large industrial complexes, the standard guides electricians in designing and implementing systems that meet strict safety protocols. Real-world applications include wiring for new housing developments, commercial buildings, and industrial factories. The 2018 edition, along with its 2020 and 2021 amendments, has been instrumental in modern projects, addressing challenges like energy efficiency and technological advancements. Case studies highlight how these rules prevent hazards and ensure compliance, making them indispensable for professionals. Practical examples demonstrate the standard’s adaptability to diverse electrical needs, reinforcing its importance in the industry. Lessons learned from projects highlight the importance of adhering to the AS 3000 Wiring Rules. Electricians have observed that strict compliance prevents electrical hazards and ensures system reliability. Projects undertaken post-2018 reveal that understanding the standard’s updates is crucial for avoiding rework and delays. For instance, the 2020 amendments clarified specific installation practices, reducing confusion and enhancing safety. Additionally, the emphasis on verification processes has improved overall system performance. These insights underscore the need for ongoing training and adherence to the Wiring Rules, benefiting both professionals and clients. By applying these lessons, future projects can achieve higher standards of safety and efficiency, aligning with the standard’s objectives. Certification programs ensure professionals master the AS 3000 Wiring Rules, enhancing their credibility and expertise in safe electrical installations, while staying updated on the latest standards. Courses on the AS 3000 Wiring Rules provide comprehensive training, enabling electricians to interpret and apply the standard effectively. These programs cover fundamental safety principles, installation practices, and compliance requirements. Many courses are designed to align with the latest amendments, such as the 2018 edition and subsequent updates; Participants gain hands-on experience with real-world scenarios, ensuring they understand key changes and their practical implications. Resources like the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF are often included to facilitate learning. These courses are essential for professionals seeking to enhance their expertise and stay compliant with current regulations, ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations across Australia and New Zealand. Certification in the AS 3000 Wiring Rules significantly enhances a professional’s credibility and career prospects. It demonstrates a deep understanding of the standard, ensuring compliance with safety and regulatory requirements. Certified professionals often experience increased earning potential and access to exclusive industry resources. Certification also provides a competitive edge, as employers prioritize qualified individuals who can navigate complex electrical installations with confidence. Additionally, it ensures professionals remain updated on the latest amendments and best practices, mitigating legal and operational risks. For those aspiring to leadership roles, certification is often a prerequisite, underscoring its importance in advancing within the electrical trade. It is a vital investment for long-term professional growth and industry recognition.8.2 Testing and Verification Processes
Compliance and Enforcement
9.1 Legal Requirements
9.2 Consequences of Non-Compliance

Resources for Electricians
10.1 Accessing the AS 3000 Wiring Rules PDF
10.2 Supplementary Materials and Guides

Frequently Asked Questions
11.1 Common Queries About the Standard
11.2 Addressing Typical Confusions
Case Studies and Examples
12.1 Real-World Applications
12.2 Lessons Learned from Projects
Training and Certification
13.1 Courses for Understanding the Standard
13.2 Certification Benefits for Professionals
